Improved Numerical Methods Reduce Spurious Mixing in MPAS-Ocean
In the ocean, vertical diffusion is several orders of magnitude smaller than horizontal diffusion. It is difficult for ocean models to reproduce low values of vertical diffusion due to spurious mixing intrinsic to the numerical algorithms. Recent work by DOE ocean model developers shows that spurious vertical mixing may be reduced by several advanced techniques.
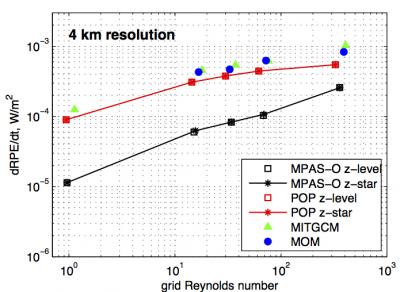
The Model for Prediction Across Scales-Ocean (MPAS-Ocean) was validated against five long-standing ocean models using five domains, ranging from simple idealized test cases to real-world simulations. MPAS-Ocean produces results commensurate with the other models, validating the functionality of the new model. In addition, MPAS-Ocean produced less spurious mixing than other models, by up to a factor of ten, as measured by the resting potential energy (RPE, see figure). This is due to a combination of the vertical coordinate, hexagon-type horizontal grid, and a tracer advection scheme designed for these grids.
Ocean models are often categorized by their vertical coordinate. The Arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian method (ALE) of the MPAS-Ocean model offers great flexibility, so that users may choose from numerous vertical coordinates: z-level (fixed), z-star (expands with sea surface), z-tilde (grid moves with fast waves), sigma (terrain-following), and idealized isopycnal (density surfaces). All of these modes were validated in idealized test cases and compared to other ocean models, including POP, MOM, MITgcm, ROMS, and HIM. The z-type coordinates were validated using real-world cases.
MPAS-Ocean performed similarly or better than long-standing ocean models, and certain configurations of the vertical coordinate dramatically reduced the spurious mixing. Thanks to improved algorithms, MPAS-Ocean will better represent physical mixing processes in climate simulations, leading to more accurate climate studies.
Petersen, M.R., D. W. Jacobsen, T. D. Ringler, M. W. Hecht, M. E. Maltrud (2015): Evaluation of the arbitrary Lagrangian–Eulerian vertical coordinate method in the MPAS-Ocean model. Ocean Modelling, Volume 86, Pages 93-113, ISSN 1463-5003, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ocemod.2014.12.004.